Introduction to Building a Business Case for VR Training
Virtual reality training is transforming how enterprises approach workforce development in the modern era. From enhancing safety in high-risk environments to improving retention rates through immersive learning with digital twin environments, VR training offers a compelling case for businesses looking to modernize their training programs. However, securing executive buy-in requires more than just enthusiasm—it demands a well-structured business case.
If you’re an L&D professional or a training manager looking to implement VR training in your organization, you need to present a strong argument backed by clear benefits, cost justifications, and strategic alignment with business objectives. This guide will walk you through the key steps to build a business case that resonates with decision-makers.
For a deep dive into the world of VR training, check out our comprehensive Ultimate Guide to VR Training.
Step 1: Identify the Problem VR Training Solves
Before proposing a VR training solution, you must first define the specific problem it addresses. Decision-makers are more likely to approve a project that directly ties into an existing business challenge. Without a clear link to business impact, executives may see VR training as an unnecessary expense rather than a strategic investment.
Key Challenges VR Training Addresses:
✅ High employee turnover due to ineffective training programs that fail to engage and retain talent.
✅ Low knowledge retention from traditional training methods, leading to repeated errors and additional retraining costs.
✅ Safety risks in hazardous work environments where employees need hands-on experience but cannot train safely in real-world conditions.
✅ Costly onboarding and training programs that require extensive travel, instructor-led sessions, and downtime for employees.
✅ Inconsistent training experiences across multiple locations, leading to disparities in skill levels and operational inefficiencies.
“Many companies hesitate to invest in new training technologies, fearing high costs and adoption barriers. However, the real cost lies in outdated methods that fail to engage employees and lead to skill gaps. VR training provides a scalable, data-driven, and immersive solution that ensures long-term workforce efficiency.”
Once you’ve identified the core issue, frame it in a way that highlights its impact on the business. Use metrics and real-world examples where possible to illustrate the problem. For example, if high employee turnover is an issue, quantify how much is being spent on hiring and retraining new employees. If safety is a concern, present statistics on workplace incidents and potential liabilities that could be reduced with VR training.
By clearly defining the problem and demonstrating how VR training addresses it, you’ll set the foundation for a persuasive business case that resonates with executives.
Step 2: Highlight the Benefits of VR Training
Executives need to see the tangible benefits of investing in VR training. A well-articulated business case should not only emphasize cost savings but also showcase improvements in workforce efficiency, safety, and engagement. Here are some of the most impactful advantages:
1. Increased Knowledge Retention and Faster Learning
Research shows that VR-based learning improves retention rates significantly compared to traditional methods. A PwC study found that employees trained in VR learn four times faster than in a classroom setting and are 275% more confident in applying their skills after training. The immersive nature of VR enhances focus and helps employees practice in a risk-free environment, leading to better long-term knowledge retention.
2. Cost Savings Over Time
While VR training requires an initial investment in hardware and software, it offers substantial long-term cost savings by eliminating travel expenses, reducing reliance on in-person instructors, and decreasing training time. Enterprises like Toyota Material Handling have realized $1.5 million in annual savings through VR training (read the full Toyota VR training case study here).
Curious about the ROI of VR training? Try out our VR Training ROI Calculator to estimate potential savings for your business.
3. Enhanced Safety and Risk Reduction
For industries that involve high-risk tasks—such as construction, energy, and manufacturing—VR training provides a controlled environment where employees can practice dangerous procedures without real-world consequences. This reduces workplace accidents, lowers insurance costs, and improves overall safety compliance.
4. Scalability and Consistency Across Locations
One of the biggest challenges with traditional training is maintaining consistency across multiple locations. VR training ensures that every employee receives the same standardized training experience, reducing knowledge gaps and improving operational efficiency across the organization. With cloud-based platforms like our homegrown Vision Portal, enterprises can centrally manage training content, track progress, engage with trainees in real-time and deploy VR modules across multiple sites globally.
5. Higher Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
Traditional training methods, such as reading manuals or attending lectures, often lead to low engagement and information retention. VR, on the other hand, provides an interactive, gamified experience that enhances employee participation. Studies show that employees who train in VR are up to 40% more engaged than those in traditional training programs. Increased engagement leads to higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates.
6. Data-Driven Insights and Performance Analytics
Modern VR training platforms come with advanced analytics tools that allow businesses to track employee performance, monitor progress, and identify skill gaps. With the Vision Portal for example, organizations can collect real-time data on training effectiveness, completion rates, and areas for improvement, helping optimize learning outcomes over time.
7. Reduced Downtime and Faster Onboarding
For industries where hands-on experience is critical, and with VR training employees can gain hands-on experience in a risk-free virtual environment before transitioning to real-world tasks, reducing errors and boosting confidence.. This shortens the onboarding process and gets employees up to speed 50% faster compared to traditional methods.
By highlighting these tangible benefits, you can build a compelling case for VR training that aligns with executive priorities such as cost reduction, operational efficiency, and employee performance.
Step 3: Provide a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost Considerations
- Hardware: VR headsets, controllers, and accessories (e.g. Meta Quest series & PICO headsets)
- Software Development: Custom training modules, CGI simulations, or licensing pre-built VR content
- Implementation Costs: IT integration, LMS compatibility, cloud-based platform setup
- Maintenance & Support: Software updates, bug fixes, cloud storage, and analytics tracking
- Employee Training & Onboarding: Teaching staff how to use and manage VR training
Potential Cost Savings
✅ Reduced travel and instructor costs – No need for in-person workshops or off-site training facilities
✅ Decreased downtime for hands-on training – Employees train asynchronously without disrupting workflow
✅ Lower risk of accidents and liability costs – Reducing safety incidents through VR simulation can lower insurance premiums
✅ Faster onboarding times leading to productivity gains – Employees gain hands-on experience in VR before entering live environments
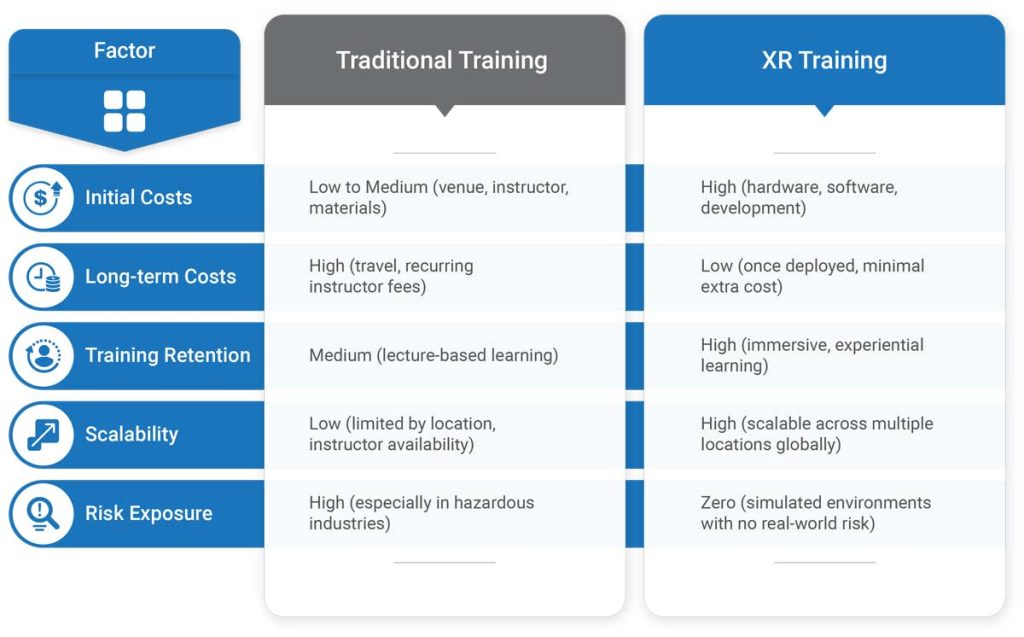
ROI & Payback Period Estimation
Using case studies from similar industries can illustrate cost savings for your organization. Many enterprises achieve a positive ROI within 12-24 months, as reduced training time, fewer workplace incidents, and lower operational costs quickly offset initial expenses.
Want to calculate your expected ROI? Try our ROI Calculator to get a customized estimate for your business case for VR training.
Step 4: Address Potential Objections
Executives may have concerns about VR training implementation. Be proactive in addressing these common objections and provide strategic solutions.
1. High Upfront Costs
Response: Many organizations hesitate due to the initial investment required for VR hardware, software, and deployment. However, VR training leads to significant long-term savings by reducing travel, instructor fees, and lost productivity from inefficient training methods. Additionally, VR training can be scaled across multiple locations, reducing per-employee training costs over time. Highlighting case studies, such as Toyota’s $1.5M in annual savings mentioned previously, can help justify the initial investment.
2. Integration Challenges with Existing Training Systems
Response: Organizations may worry about whether VR training will integrate with their current Learning Management System. Many modern VR training platforms are LMS-compatible and allow organizations to seamlessly track employee progress, completion rates, and performance analytics. This ensures a smooth transition without disrupting existing workflows.
3. Technology Adoption Barriers
Response: Some executives fear that employees may resist adopting VR due to unfamiliarity with the technology. However, modern VR headsets like the Meta Quest lineup and Pico NEO’s are increasingly more intuitive and user-friendly than earlier generations, and the technology will only to continue to improve over time. A gradual rollout strategy, starting with a small pilot program, can help organizations ease adoption, address concerns, and refine training before full-scale deployment.
4. Concerns About Training Effectiveness
Response: Decision-makers may question whether VR training is as effective as traditional training. However, research shows that VR learners retain information 4x faster than classroom learners and demonstrate higher confidence in applying their skills. Additionally, industries such as energy & utilities, manufacturing, defense and healthcare are already successfully using VR to improve safety and operational training. Providing real-world success stories and metrics can help alleviate concerns about effectiveness.
Step 5: Propose a Pilot Program
Rather than requesting immediate large-scale adoption, proposing a pilot program can help mitigate risk and demonstrate measurable success before full implementation. This can help you build a strong business case for VR training internally.
How to Structure a Pilot Program:
1️⃣ Select a training module or department best suited for VR training.
2️⃣ Define clear success metrics – engagement, retention, skill competency.
3️⃣ Gather feedback & refine training based on participant experiences.
4️⃣ Present tangible results to decision-makers for broader implementation.
🔎 A successful pilot acts as a proof of concept (POC), paving the way for full-scale adoption.
Conclusion on Building a Business Case for VR Training
Building a strong business case for VR training isn’t just about numbers—it’s about solving real challenges, proving the value, and getting buy-in from decision-makers. The key is to focus on how immersive learning makes work safer, faster, and more effective while aligning with your company’s goals.
At its core, VR training isn’t just a cost-cutting tool—it’s a way to innovate, reduce risk, and build a future-ready workforce. Companies that embrace it now will have the edge in developing top talent for years to come.
Here’s what makes a strong case for VR training:
- Solve real business problems – Show how it tackles pain points and improves workflows.
- Prove the ROI – Highlight cost savings, efficiency gains, and better learning outcomes.
- Align with company goals – Make sure it fits into the bigger picture of growth and success.
The companies that invest in immersive learning today will lead their industries tomorrow.
📅 Ready to take the next step? Schedule a demo with VR Vision today and see how building a business case for VR training can transform your workforce! 🚀